Linear Accelerator
Home > Radiation Protection and Quality Assurance >Equipment Use & Quality Assurance > Components and Operation > Linear accelerator
Can we please get your advice on this one question?
Linear Accelerator is one of the latest technologies in the treatment of cancer. The unique advantage of linear accelerator is not a radioisotope when we are shifting this type of instruments much care is not required however, attention is always required. The name linear accelerator is come from its own part; linear accelerator tube is used to accelerate the high energy charged particles in the wave guide by high frequency electromagnetic waves. The significant portions will be discussed here. They are,
Magnetron
Klystron
Beam collimation and Monitoring
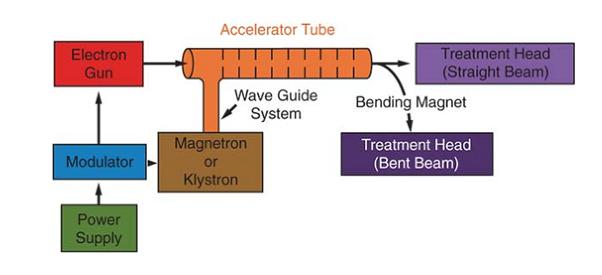
The typical diagram of linear accelerators
Magnetron:
The magnetron is a device that produces microwaves. It functions as a high-power oscillator, generating microwave pulses of several microseconds' duration and with a repetition rate of several hundred pulses per second. The frequency of the microwaves within each pulse is about 3,000 MHz. The magnetron has a cylindrical construction, having a central cathode and an outer anode with resonant cavities machined out of a solid piece of copper. The space between the cathode and the anode is evacuated. The cathode is heated by an inner filament and the electrons are generated by thermionic emission. A static magnetic field is applied perpendicular to the plane of the cross section of the cavities and a pulsed DC electric field is applied between the cathode and the anode. The electrons emitted from the cathode are accelerated toward the anode by the action of the pulsed DC electric field. Under the simultaneous influence of the magnetic field, the electrons move in complex spirals toward the resonant cavities, radiating energy in the form of microwaves. The generated microwave pulses are led to the accelerator structure via the waveguide. Typically, magnetrons operate at 2 MW peak power output to power low-energy linacs (6 MV or less). Although most higher-energy linacs use klystrons, accelerators of energy as high as 25 MeV have been designed to use magnetrons of about 5 MW power.
Klystron:
Klystron is not a source microwaves rather than it is a amplifier of microwaves. It is driven by source of low energy oscillators. The electrons produced by the cathode are accelerated by a negative pulse of voltage into the first cavity, called the buncher cavity, which is energized by low-power microwaves. The microwaves set up an alternating electric field across the cavity. The velocity of the electrons is altered by the action of this electric field to a varying degree by a process known as velocity modulation. Some electrons are speeded up while others are slowed down and some are unaffected. This results in bunching of electrons as the velocity-modulated beam passes through a field-free space in the drift tube. As the electron bunches arrive at the catcher cavity, they induce charges on the ends of the cavity and thereby generate a retarding electric field. The electrons suffer deceleration, and by the principle of conservation of energy, the kinetic energy of electrons is converted into high-power microwaves. Typically, magnetrons operate at 2 MW peak power output to power low-energy linacs (6 MV or less). Although most higher-energy linacs use klystrons, accelerators of energy as high as 25 MeV have been designed to use magnetrons of about 5 MW power.
Beam collimation and Monitoring:
Beam collimation is also one of the significant parts in the machine. After ejected from the target X ray are guided through the flattening filter to get the homogenous distribution in the treatment area and also to harden the beam. After that the collimators are the one defining the field size will guide the radiation into the desire area of the target. Two dose monitoring chambers are fixed after the flattening filter before the collimator to monitor the dose. This is sealed and also not affected by the radiation.
Questions:
1. What is the frequency of the microwaves produced in the magnetron?
a) 3000 MHZ
b) 300MHZ
c) 30000MHZ
d) None of these
2. Klystron is
a) Low energy microwaves producer
b) High energy microwaves producer
c) A source of microwave amplifier
d) All
Answer:
1. a) 3000MHZ
2. c) A source of microwave amplifier
References:
1. The Physics of Radiation Therapy, 4th Edition by Faiz.M.Khan
2. www.wikipedia.com
Home > Radiation Protection and Quality Assurance >Equipment Use & Quality Assurance > Components and Operation > Linear accelerator
FREE Infographic What successful people believe. What successful people do
Dictionary of Cancer Terms
Need help understanding a word? Here is an electronic resource that gives meaning to Cancer terms and their usage.

StrengthsFinder 2.0