Pancreas Adrenal liver and Gallbladder
Home > Clinical Concepts In Radiation Oncology > Anatomy, Physiology > Abdomen,Pelvis, GI and GU > Pancreas, adrenal etc
Can we please get your advice on this one question?
Pancreas:
The cells which make up the pancreatic islets (islets of Langerhans) are found in clusters irregularly distributed throughout the substance of the pancreas. Unlike the exocrine pancreas, which produces pancreatic juice, there are no ducts leading from the clusters of islet cells. Pancreatic hormones are secreted directly into the bloodstream and circulate throughout the body. There are three main types of cells in the pancreatic islets:
(alpha) cells that secrete glucagon
(beta) cells that secrete insulin
5 (delta) cells that secrete somatostatin
The normal blood glucose level is between 2.5 and 5.3 mmol/litre (45 to 95 mg/100 ml). Blood glucose levels are controlled mainly by the opposing actions of insulin and glucagon,
Glucagon increases blood glucose levels
Insulin reduces blood glucose levels.
Adrenal gland:
There are two adrenal glands, one situated on the upper pole of each kidney enclosed within the renal fascia. They are about 4 cm long and 3 cm thick. The arterial blood supply to the glands is by branches from the abdominal aorta and renal arteries. The venous return is by suprarenal veins. The right gland drains into the inferior vena cava and the left into the left renal vein. The glands are composed of two parts which have different structures and functions. The outer part is the cortex and the inner part the medulla. The adrenal cortex is essential to life but the medulla is not.
Functions:
The adrenal glands are comprised of two parts--the cortex and medulla--that produce hormones (chemicals messengers that regulate body functions). The medulla, or inner part of the adrenal glands, produces the hormones norepinephrine and epinephrine, which regulate the "fight or flight" response in the body, the body's reaction to stressful events. The cortex, the outer portion of the adrenal glands, produces several hormones that affect blood pressure and blood sugar levels, growth, as well as some sexual characteristics.
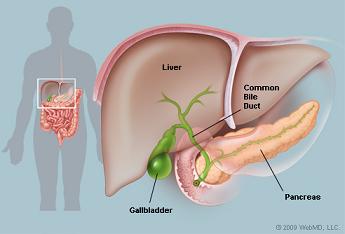
Liver:
The liver is a large, meaty organ that sits on the right side of the belly (see figure a). Weighing about 3 pounds, the liver is reddish-brown in color and feels rubbery to the touch. Normally you can't feel the liver, because it's protected by the rib cage. The liver has two large sections, called the right and the left lobes. The gallbladder sits under the liver, along with parts of the pancreas and intestines. The liver and these organs work together to digest, absorb, and process food. The liver's main job is to filter the blood coming from the digestive tract, before passing it to the rest of the body. The liver also detoxifies chemicals and metabolizes drugs. As it does so, the liver secretes bile that ends up back in the intestines. The liver also makes proteins important for blood clotting and other functions.
Gall bladder:
The gallbladder is a small pouch that sits just under the liver (fig a). The gallbladder stores bile produced by the liver. After meals, the gallbladder is empty and flat, like a deflated balloon. Before a meal, the gallbladder may be full of bile and about the size of a small pear. In response to signals, the gallbladder squeezes stored bile into the small intestine through a series of tubes called ducts. Bile helps digest fats, but the gallbladder itself is not essential. Removing the gallbladder in an otherwise healthy individual typically causes no observable problems with health or digestion yet there may be a small risk of diarrhea and fat malabsorption.
Questions:
1) What is the function of pancreas
a) Maintain the blood sugar levels
b) Secrets t5
c) Secrets sex hormones
d) All
2) What is the function of liver?
a) Filter the blood from digestive tract
b) Detoxifies of chemicals and drugs
c) Secrets bile
d) Producing protein for blood clotting
e) All
Answer:
a) Maintain the blood sugar levels
e) All
References:
2. https://upload.wikimedia.org
4. Ross and Wilson, Anatomy and physiology in health and illness by Anne Waugh and Allison Grant.
Home > Clinical Concepts In Radiation Oncology > Anatomy, Physiology > Abdomen,Pelvis, GI and GU > Pancreas, adrenal etc
FREE Infographic What successful people believe. What successful people do
Dictionary of Cancer Terms
Need help understanding a word? Here is an electronic resource that gives meaning to Cancer terms and their usage.

StrengthsFinder 2.0