Radiation Therapy
Home > Clinical Concepts In Radiation Oncology >Treatment Options > Radiation Therapy
Can we please get your advice on this one question?
Radiation Therapy:
In radiation therapy (also called radiotherapy), high-energy X or gamma rays are used to destroy the cancer cells and stop them from growing and dividing.
Types of radiation therapy:
Treatment for cancer consists of three major parts such as surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy. In general the radiation treatment will be prescribed alone or in combine with the surgery and chemotherapy to achieve the extended benefit of treatment. In this type of treatment it, affects cancer cells only in the treated area. Radiation may deliver to the patient externally i.e. from a machine fig: a (external radiation). It can also come from an implant (a small container of radioactive material) placed directly into or near the tumour (internal radiation or brachytherapy). Some patients receive combination of both modalities for the treatment.
External Beam Radiation Therapy:
External radiation therapy is usually given on an outpatient basis in a hospital or clinic 5 days a week for a number of weeks. Patients are not radioactive during or after the treatment.


Fig a shows the treatment machines
Brachytherapy or Internal radiation therapy:
In brachytherapy therapy, the patient stays in the hospital for a few days. The implant may be temporary or permanent. Because the level of radiation is highest during the hospital stay, patients may not be able to have visitors or may have visitors only for a short time. Once an implant is removed, there is no radioactivity in the body. The amount of radiation in a permanent implant goes down to a safe level before the patient leaves the hospital.
Due to development of technology in the field of brachytherapy now a days patients are treated as outpatient basis like external beam therapy.
Side effects of radiation therapy:
With radiation therapy, the side effects depend on the treatment dose and the part of the body that is treated. The most common side effects are tiredness, skin reactions Fig: b (such as a rash or redness, permanent pigmentation, and scarring) in the treated area, and loss of appetite. Radiation therapy can cause inflammation of tissues and organs in and around the body site radiated. This can cause symptoms that depend on what organs are affected and to what degree. For example, radiation can inflame skin to cause a burn or permanent pigmentation. It can also irritate the colon and cause diarrhoea. Radiation therapy can also cause a decrease in the number of white blood cells; cells that help protect the body against infection.
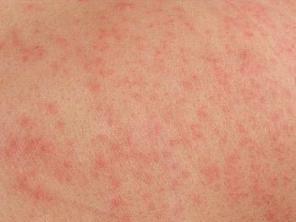
Fig: b shows the skin reaction due to radiation therapy
Although the side effects of radiation therapy can be unpleasant, they can usually be treated or controlled. It also helps to know that, in most cases, they are not permanent. To a great degree, the possible side effects of radiation therapy depend on the location and the amount of radiation.
Questions:
1. What are the general side effects of radiation therapy?
a) Skin reactions
b) Tiredness
c) Scarring
d) Loss of appetite
e) All
2. Radiation therapy has significant benefits and notable effects also.
a) True
b) False
Answers:
1. e) All
a) True
References:
2. https://www.medicinenet.com/script/main/hp.asp
5. http://www.aboutbrachytherapy.com
Home > Clinical Concepts In Radiation Oncology >Treatment Options > Radiation Therapy
FREE Infographic What successful people believe. What successful people do
Dictionary of Cancer Terms
Need help understanding a word? Here is an electronic resource that gives meaning to Cancer terms and their usage.

StrengthsFinder 2.0
