Adverse Effects
Home > Clinical Concepts In Radiation Oncology > Radiation Tissue Tolerance > Adverse Effects
Can we please get your advice on this one question?
Radiation is used along with surgery and chemotherapy to treat cancer. It works by damaging the DNA inside a tumour cell so that the cell is unable to continue growing. At least half of all cancer patients will receive radiation at some stage during their battle with cancer. Adverse reactions may be felt as early as a few days or weeks after radiation treatments have begun, and as long as a few years after treatments have ended.
The three most commonly experienced side effects of radiation therapy are
- Fatigue: Fatigue, or a general sense of tiredness, remains the most common adverse side effect of radiation therapy. The fatigue probably results due to the significant amount of energy the body utilize to heal itself after the radiotherapy. Fatigue begins about two weeks after the therapy begins. This side effect can last for a few weeks after treatment or up to a year.
- Skin Problems: The skin that has been exposed to treatment may appear red, sunburned, tan or irritated. The skin is sensitive and should be treated as so. You can request special creams/gels from your doctor or oncology nurse (there is one called Radiagel, for example). Patients should avoid perfumes or scented body lotions, tight-fitting clothing, and exposing the area to sun (during treatment and for at least one year after). Problems with the skin will go away after treatment ends.
- Loss of Appetite: Loss of appetite can lead to fatigue and nutritional deficiencies. It is important to keep up strength during any cancer treatment and food is one of the best resources to do that. Smaller meals throughout the day instead of three square meals help. Eating foods rich in vitamins like fruits and veggies are essential. Appetite will increase as treatment ends. For patients undergoing treatment for head or neck cancer (and sometimes lung), lack of saliva can be a side effect.
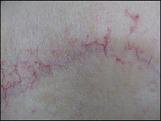
Figure a: Telangiectasis in a 73-year-old woman who completed external beam radiation therapy three and one half years earlier for an infiltrating ductal carcinoma of the right breast (T4N2M0; stage IIIB). Treatments included radiation to the chest wall, supraclavicular area, and posterior axilla (5,040 cGy), followed by an electron boost to the incision line (1,440 cGy).
Other Radiation Side Effects
This depends on what type of cancer and in which you receive treatment on your body. Possible side effects include:Hair Loss:
Hair loss only occurs at the site which is being treated. If you are having radiation therapy on pelvis, there will no loss of hair on the head. But, if they are having treatment for head and neck cancer, there will be a experience hair loss. The good news is that in most cases, hair does grow back after treatment.
Decreases in Blood Count:
Radiation can cause the lowering of white blood cells and platelets. This can lead to lowered immunity to viruses and bacteria because the white blood cells are what fights off these attackers. Tests will be done on a regular basis to check blood counts and treatment may be altered depending on the results. While side effects do vary with treatment, where the radiation is being directed will produce different side effects. For instance, treatment to the pelvis may cause fertility problems, and treatment to the head and neck can produce dental problems like cavities.
Questions:
1. What are the three main significant adverse effects in radiation therapy?
a) Fatigue
b) Loss of appetite
c) Skin problems
d) all
2. Due to radiation blood count in the body will increase or decrease
a) increase
b) decrease
c) first increase and then decrease
d) none
Answer:
1. d) all
2. b) decrease
Reference:
Home > Clinical Concepts In Radiation Oncology > Radiation Tissue Tolerance > Adverse Effects
FREE Infographic What successful people believe. What successful people do
Dictionary of Cancer Terms
Need help understanding a word? Here is an electronic resource that gives meaning to Cancer terms and their usage.

StrengthsFinder 2.0
